The Registered Retirement Savings Plan (RRSP) is one of the most popular financial tools in Canada. But it’s more than just a savings account—it’s a powerful strategy to plan for retirement and reduce your tax burden. With clear benefits and some disadvantages, understanding how the RRSP works and how to integrate it with other tools like the Tax-Free Savings Account (TFSA) can be the key to long-term financial success.
What is the RRSP, and How Does It Work?
The RRSP is a government-registered plan that allows you to save for retirement while reducing your taxes now.
Here’s how it works step by step:
Tax-Deductible Contributions:
Contributions made to your RRSP reduce your taxable income for the year.Example: If you earn $80,000 and contribute $10,000 to your RRSP, you will only be taxed on $70,000.
Tax-Free Growth:
Investments within the RRSP grow tax-free while they remain in the account.Taxable Withdrawals:
During retirement, withdrawals are taxed as income. Ideally, you’ll be in a lower tax bracket during this phase, meaning you pay less tax.
Advantages of the RRSP
Immediate Tax Savings:
Contributions to the RRSP provide an income tax deduction, potentially resulting in a significant refund.Tax-Free Growth:
Investments like stocks, mutual funds, and GICs within the RRSP grow without annual taxes on dividends or capital gains.Strategic Tax Planning:
Ideal for those in a high tax bracket now, who expect to be in a lower one during retirement, resulting in long-term tax savings.Special Programs:
Leverage the Home Buyers’ Plan (HBP) to withdraw up to $35,000 (or $70,000 for a couple) for a home purchase, or the Lifelong Learning Plan (LLP) to fund education, as long as repayment rules are followed.Contribution Flexibility:
Unused contribution room carries forward to future years, allowing for larger contributions later.
Disadvantages of the RRSP
Taxable Withdrawals:
All funds withdrawn, including earnings, are taxed as income in the year of withdrawal. Poor planning could lead to a high tax burden.Contribution Limits:
Annual contribution limits are capped at 18% of your earned income, up to a maximum of $30,780 in 2025.Limited Flexibility:
Withdrawals outside the HBP or LLP programs are subject to withholding tax and increase taxable income.Impact on Retirement Benefits:
Large RRSP withdrawals during retirement can reduce benefits like Old Age Security (OAS) due to the clawback mechanism.Focus on Taxation:
While tax benefits are significant, the RRSP may not suit everyone. Alternatives like the TFSA could be more advantageous depending on your financial situation and goals.
RRSP vs. TFSA: How to Choose?
Both the RRSP and TFSA are valuable tolos, but they serve different purposes.
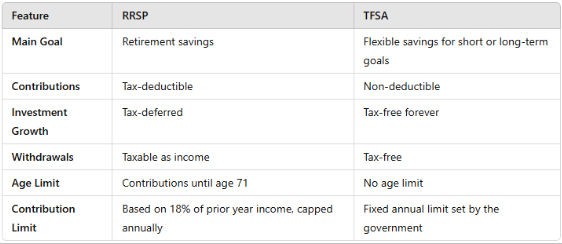
When to Choose the RRSP?
The RRSP is ideal for:
Immediate Tax Reduction:
If you’re in a high tax bracket, RRSP contributions reduce your tax burden now.Example: A taxpayer earning $90,000 who contributes $10,000 could save up to $3,000 in taxes, depending on the province.
Retirement Focus:
Invest for the future while benefiting from tax-free compound growth.Employer Matching Contributions:
If your employer offers matching contributions to your RRSP, maximize this benefit—it’s like getting free money!Long-Term Planning:
Withdraw during retirement in a lower tax bracket to optimize tax savings.
When to Opt for the TFSA?
The TFSA is the better choice for:
Flexible Savings:
Ideal for emergencies or short-term goals like buying a car or going on a trip.Withdrawals are tax-free and do not affect your contribution room in the following year.
Lower Current Income:
If you’re in a low tax bracket, the TFSA offers more benefits, as RRSP deductions provide minimal tax relief.Diversified Investments:
Use the TFSA to complement long-term growth with tax-free withdrawals.Unaffected Benefits:
TFSA withdrawals do not impact government benefits like OAS, unlike large RRSP withdrawals that could trigger the clawback.
Strategic Combination: RRSP and TFSA
For many Canadians, combining RRSP and TFSA accounts provides the best of both worlds.
Use the RRSP to Reduce Taxes:
Contribute during high-income years to lower your taxable income.Reinvest RRSP Refunds in the TFSA:
Use your tax refund from RRSP contributions to build a tax-free emergency fund.Diversify Retirement Income:
Withdraw from the RRSP strategically to stay below clawback thresholds and supplement with tax-free TFSA withdrawals.Start with TFSA, Then Move to RRSP:
If you’re in a lower tax bracket now, prioritize the TFSA. As your income grows, shift focus to the RRSP for greater tax savings.
Example Scenario
A couple, aged 45, earning $85,000 and $50,000 annually:
They maximize RRSP contributions to reduce taxes and invest their refunds in the TFSA.
At 65, the RRSP is converted to a Registered Retirement Income Fund (RRIF) for regular income, while the TFSA supplements this income tax-free.
Result: A diversified, optimized plan to minimize taxes now and during retirement.
RRSP and TFSA Statistics
Adoption: 46% of Canadians contribute to a TFSA, while 35% invest in RRSPs.
Growth Rates: TFSA balances grow by approximately 10% annually, driven by increased limits and popularity.
2025 Limits: TFSA annual contribution limit: $6,500; RRSP annual limit: $30,780.
Tips to Maximize RRSP Benefits
Start Early:
Small, regular contributions benefit significantly from compound interest over time.Automate Contributions:
Set up monthly contributions to avoid last-minute stress.Employer Matching:
Take full advantage of matching contributions from your employer.Plan Withdrawals Strategically:
During retirement, withdraw funds in a way that minimizes tax impacts.
Conclusion: Is the RRSP Right for You?
The RRSP is a powerful tool for saving taxes and building a solid financial future. However, it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution. Understanding its benefits, drawbacks, and how to combine it with the TFSA ensures you meet your financial goals efficiently.
📩 Need help creating the best strategy with your RRSP and TFSA?
MB Tax Solutions is here to assist!
📱 WhatsApp: +1 647-856-6289
📧 Email: info@mbtaxsolutions.com
💻 Schedule a consultation: Click Here
#RRSP #TFSA #FinancialPlanning #MBTaxSolutions #RetirementInCanada #WealthManagement



 Precisa de ajuda para criar a melhor estratégia com o RRSP e TFSA?
Precisa de ajuda para criar a melhor estratégia com o RRSP e TFSA? WhatsApp: +1 647-856-6289
WhatsApp: +1 647-856-6289
